A significant decrease in monkeypox cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo
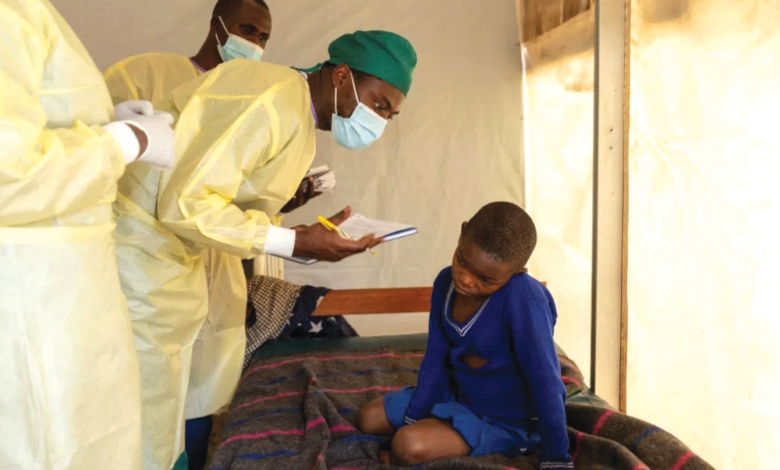
The Democratic Republic of Congo has recorded a significant and positive health development on the African continent, with the country's National Institute of Public Health announcing a marked and substantial decrease in the number of monkeypox (Mpox) cases. This announcement bolsters hopes for controlling the epidemic, which has posed a major challenge to both local and international health systems in recent months.
Record drop in weekly infection rates
According to official data from the institute, the weekly infection rate has seen a dramatic decline, dropping from around 2,000 cases per week at the peak of the outbreak to only between 250 and 300 cases . This significant decrease reflects the effectiveness of the measures taken to contain the virus and limit its spread among the population.
In detailing this epidemiological improvement, Christian Ngendo, coordinator of the Public Health Emergency Operations Center, explained that the disease's spread has significantly narrowed. While the epidemic was present in 401 health zones at the start of the outbreak, cases recorded during December were limited to 19 health zones . Ngendo noted that most active cases are currently concentrated in specific regions, namely North and South Kivu, as well as some areas in Sankoro, which facilitates focusing surveillance and health intervention efforts on these remaining hotspots.
General context and global importance of the event
These figures are particularly significant given the Democratic Republic of Congo's historical status as a major epicenter of the disease. Monkeypox is a zoonotic viral disease, and the Congo has suffered for years from the most virulent strain (Clade I). Previous spikes in cases had already alarmed the World Health Organization and the international community, who feared that local outbreaks could escalate into a wider regional pandemic, especially given the weak health infrastructure in some remote areas.
Expected impact and ongoing efforts
This decline is a vital indicator of the success of epidemiological surveillance strategies, community awareness campaigns, and medical interventions led by local authorities with the support of international partners. Controlling the epidemic in the Democratic Republic of Congo not only protects the local population but also directly contributes to strengthening global health security by reducing the likelihood of cross-border transmission to neighboring countries or other continents.
Despite these promising results, experts stress the need to remain vigilant and cautious, especially in areas that still have active cases, such as the Kivu region, to ensure the complete elimination of outbreak hotspots and prevent any future resurgence of the virus.




